Global Strategy and Implementation of Coca-Cola.
Coca-Cola Company is a well-known multinational corporation that deals with the area of beverage. Its turnover in the last financial report is 11.3 billion dollars. Having a worldwide presence, Coca-Cola operates in over 200 countries and is one of the most far-flung beverage companies on the planet.
The company has a globally diversified workforce with 79,100 employees representing a wide range of functions and locations in 2024. In this study, we explore the global strategy, development, and implementation structure of Coca-Cola, specifically considering its strategies, theoretical frameworks, and related business examples for critical evaluation.
Read more: Financial Controller of Coca-Cola Company
Bargaining Power of Suppliers
Moderate Bargaining Power
Raw material suppliers that include the likes of sugar producers, packaging manufacturers, and flavor suppliers, generally operate in a moderate bargaining power range in the sectors which they operate. While they can well be of a support they also have numerous alternatives, which makes reaching monopsony state pretty difficult.
Impact of Commodity Price Fluctuations
Fluctuations in commodity prices (sugar and aluminum), the higher they are, the more costs are on the beverage producers. This volatility is associated with revenues and may therefore determine brands’ value management thinking product positioning or pricing.
Limited Supplier Options for Key Ingredients
limited access provides the suppliers and few terms and conditions more control often because the ingredient is highly priced or packaged accordingly and essential to the products’ formulation.
Moderate Switching Costs
However, the switching costs for competitors may still be moderate as there may be alternative distributors they can still get supplies from. The process of fostering the new supply partners with regard to the qualification, negotiation as well as the logistics coordination in essence is very demanding in terms of resources and time.
While the strong bargaining position of the buyer is alleviated by the other suppliers, there is a reassurance that no single supplier can impose its powers over all the market.
Potential for Forward Integration
Suppliers can be interested in attaining a vertically integrated bargaining power, enabling their further directions in retail channels. An alternative distribution channel will allow suppliers through the cut out of beverage companies and reaching out to retail shops to have total control of pricing and distribution, which will lead to profit margin losses and market share reduction of the beverage manufacturers.
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Considerable Bargaining Power of Large Retail Chains
Bulk purchases by mega-retail stores, supermarkets, and convenience shops make the negotiation process very leasable for them due to huge order amounts. They may strike deals with beverage manufacturers to get more not only, prices that are lower, anything, but also, better terms, affecting the manufacturers’ profitability, that is all it is.
Price Sensitivity Among Consumers
The consumers’ having a price threshold drives the beverage industry into changing production process models to provide a better offer. To continue being competitive they need to strike a balance between keeping a profit and feeding the demand for low-cost products.
Availability of Substitute Products
This situation is complex, as the demand for soft drinks is undifferentiated, and there are other alternatives available, including private-label beverages. If a beverage company petitions an increase in prices or fails to deliver on consumer preferences, buyers to can easily choose to purchase from another brand or product category.
Impact of Health Consciousness
As a result of growing health awareness among consumers, their choice gets more and more focused on products, which are healthier beverages. This phenomenon becomes particularly significant for soft drink manufacturers’ commodity mix and marketing strategies because they must be flexible enough to experience the taste change of the customers and to remain competitive with their rivals.
Influence of Brand Loyalty and Advertising
High brand loyalty by companies like Coca-Cola affects consumer preferences and weakens to some extent buyer power which guarantees a fight for market share. Assuming that the brand has strong recognition and is indirectly associated with desirability, then the consumer may turn out to be less price sensitive while also being ready to buy branded goods even when the alternative ones may be available for a lower cost.
Analysis
Porter’s Diamond Model Analysis
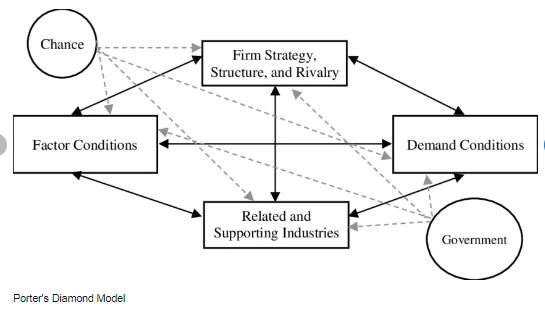
| Factor | Analysis |
| Factor Conditions | Coca-Cola benefits from advanced factors such as technology and skilled labor in its home country, the United States, which enhance its competitive advantage. |
| Demand Conditions | The strong demand for soft drinks globally provides Coca-Cola with a significant market opportunity, allowing it to leverage its brand strength and innovation capabilities. |
| Related and Supporting Industries | Coca-Cola has a network of suppliers and bottling partners worldwide, contributing to the efficiency and innovation in its value chain. |
| Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry | Coca-Cola’s aggressive marketing, innovation, and strategic alliances contribute to its competitiveness, while intense rivalry in the industry drives continuous improvement. |
| Chance | Coca-Cola is struggling with a situation of chance, which could be represented by variations of consumers preferences, changes in global economic conditions, catastrophic weather conditions or new, world’s breaking technologies by competitors |
| Government | The Coca-Cola Company basically transacts business in various countries with varying regulations in relation to product labeling, advertising, taxation, and environmental sustainability. |
Factor Conditions:
The United States serves as a crucial source of Coca-Cola’s advanced factor conditions; thus, Coke is highly favored by the company. The nation has the advanced technology, a workforce with a broad skillset, and the modern physical structure. Such factors, therefore, provide Coca-Cola with an edge in the various business elements.
For instance, technological invention is innovative enough and that is why the Coca-Cola Company can introduce new flavors, package innovations and technological advancements in its production. An access to a skilled labor force positions the company well to participate in marketing methods, brand management, and research and development functions. Another aspect is the wide-spread of the modern infrastructure, which enable delivery of products reach to tiniest areas of the most remote corner of our world.
Demand Conditions:
Worldwide demand for soft drinks serves as a signifier of Coca-Cola’s success in the global market. This growth is fueled by the changing pattern of consumer demands, the evolving lifestyle inclinations, and the rapid suburbanization, which are the common trends across the globe.
Coca-Cola is very successful in fulfilling the need for refreshments with its Coke brand, which ranks as one of the strongest brands globally, as well as an extensive patented portfolio of products that makes it possible to seize similar opportunities in many important markets worldwide. The company is thus able to broaden the range of its products and design marketing campaigns that suit different consumer groups of different regions.
Related and Supporting Industries:
Coca-Cola has built up a solid global supply chain system which is composed of suppliers, fountain operators and distributors. This network is a vital source of contribution to the improvement of supply chain efficiency of the company as well as time deliveries of the raw materials, fast manufacturing process and employment of uninterrupted distribution way down to the consumers all round the globe.
By extending its reach to a throng of suppliers and bottling partners sends the message that Coca-Cola makes proper use of competence and resources to drive its operations and compete favorably in the beverage market.
Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry:
Indeed, the strategic thrust of Coca Cola is innovative and it is marked by a lot of aggressive marketing with strategic partnerships. The company sees research and development as the essential area to invest its revenue in and produce new goods, re-invent the current ones, and enhance operational effectiveness.
In addition to this, Coca-Cola brand is one of the most powerful marketing tools with global reach, through which the company is introduced to consumers using its famous product name and then aided by different advertising avenues, such as sponsorships and promotions.
Coca-Cola continues to be a market leader in the beverage industry despite intense competition from other players such as PepsiCo due to its strong brand equity, wide distribution network, and global footprint. Through constant adjustments of its strategies, investments in innovation, and creation of strategic alliances, Coca-Cola continues to be well-placed to undergo competitive challenges and grow in the global market.
Chance
By chance factors, I mean the attributes of the situation that are external and irrelevant to the company but have a direct impact on its competitiveness. Sometimes Coca-Cola is struggling with a situation of chance, which could be represented by variations of consumer’s preferences, changes in global economic conditions, catastrophic weather conditions or new, world’s breaking technologies by competitors.
This plays a part in shaping the potential of Coca-Cola and requires the company to have a flexible mindset ensuring it becomes successful in the changing landscape of beverages. It is likely that which affects the return on investments of the market, Coca-Cola easily detects and reacts by taking advantage of the opportunities and avoiding risks that may occur in order to keep the company competitive in the global market.
Government
The processes referred as the Government factors involve the rules and guidelines imposed by governments, as well as their policies and actions, which affect a company’s operations and competitiveness. The Coca-Cola Company basically transacts business in various countries with varying regulations in relation to product labeling, advertising, taxation, and environmental sustainability. Government can also bring trade barriers, intellectual property rights and labour laws policies, which can be hindered for production costs, market access and finally strategy at all.
Through comprehending and complying with the government’s regulations as well as lobbying for characteristics, Coca-Cola can attain market capitalization despite the regulations by making market opportunities. Moreover, by creating this goodwill along with government and the key stakeholders, Coca-Cola can have a solid and improved position in global beverage business.
Bartlett & Ghoshal Framework Analysis
International Strategy
In the global beverage sector, enterprises are challenging the status quo with their first footsteps taken across the boundary of international strategy. By focusing on standardization of the products and the marketing strategy across the different markets, a considerable reduction of the costs is possible, and consequently, it is possible to build a global brand identity.
They for this purpose use copying of their well-proven formulas and brand strategies to target new markets, where they can limit the market entry risks while taking maximum benefit. In this way, companies can effectively uncover new market opportunities and make sure that their brand message resonates with the target market, which strong brand recognition and engagement is essential for the beverage industry.
Global Strategy
This growing market share might make companies consider a move to the global strategy as the allure of additional revenue become irresistible. It includes unifying authority and correlations within international concern to maintain unification and efficiency in operative activities on the scale of the planet. When companies strive to achieve uniformity in their products and processes to reap economies of scale, they also alter them regionally to create their localized versions to meet the tastes of different markets and regulatory obligations in different markets.
Tendency of adapting in beverage sector is an inevitable thing since the taste of the consumer might be diverse from one market to another. Implementing standardization principles becomes the way for the beverage producers to achieve economies of scale, decrease expenses and ensure their products are known for uniformity in the different markets that they exist in and also these economies of scale enable companies to expand their customer base and become competitive.
Transnational Strategy
In regard to the beverage industry, firms like Coca-Cola very often coordinate their businesses by employing a transnational strategy to blend global network and local adaptability. This approach emphasizes the efficacy of operating on an international level to make processes more efficient and more innovative on the one hand, but it also pays attention to how local adaptation is needed to meet the needs of various customers with different preferences, cultural practices and regulations on the other hand.
The drinks industry is engaged in factors of market varies like marketing campaign, products and operations by which they can remain to lead in garnering profit and efficiency amidst the global competition. It also enables them to use their international positioning while creating taste for local culture in the meantime, which as a result give more pleasurable and consistent experiences for customers and thus greater loyalty to the brands through the changing and competitive industry.
Operational Strategy
Within the operational strategy, Coca-Cola is going to show its readiness to continual innovations rammed within the global regulatory framework. This is realized through diverse product portfolios with introductions of new products and new regional adaptions along with maintaining an all-embracing global brand name.
Coca-Cola engages in a profound market research, which helps to discover cultures’ delicate nuances and the pattern of consumer behavior in all markets, and which in turn provides for development of industry-specific advertising campaigns and channels of distribution and sales. Such market-specific activities deliver not only relevance and resonance with the local customer but also present a strong competitive business card and share in the diverse and ever-evolving beverage industry.
Multidomestic Strategy
In markets where cultural or regulatory differences are present (singular), the beverage producers may take a multidomestic strategy. The underlying idea revolves around designing and utilizing your products as well as promotional campaigns according to the feature of specific regional markets in order to make way for more agility and adaptability.
Hence, these beverage companies present localized versions of the products, marketing that is nationally tailored to the country and specialized distribution channels so that the region that does not perform well through standardization will not be the case. This is the strategy that gives beverage companies an edge in the consumer market segmentation. By employing this strategy, these companies will be able to proffer customized products that address the unique needs of consumers in each market to drive long term growth and profitability while still maintaining strong market position.
External Environment
PESTEL Analysis
Political Factors
Coca-Cola operates in numerous countries, each having different regulations regarding the beverage industry. Political instability or government policy changes in the areas of taxation, health regulations, and environmental standards can cause Coca-Cola’s operations and profitability to be affected.
International trade agreements or tariffs adjustments can affect Coca-Cola’s global supply chain, production costs and market access. Trade conflicts or protectionist actions may interrupt the company’s supply of raw materials and distribution of products in an effective manner.
Economic Factors
Global economic conditions, which include recession or economic downturn, cause changes in consumer spending behavior and purchasing power. Consumer discretionary income that is reduced may result in lower demand for the products of Coca-Cola which will affect its sales and revenue.
The international reach of Coca-Cola makes it vulnerable to the exchange rate fluctuations. The company’s financial performance is affected by volatility in foreign exchange markets, especially in terms of revenue from international markets and translation of profits back to home currency.
Social Factors
The rising consumer consciousness of health and wellness issues, including obesity and sugar consumption, has resulted in a change in preferences to healthier drink alternatives. Coca-Cola has to overcome the challenge of how to transform its product portfolio to suit modern consumer tastes and at the same time, retain the appeal of its core brands.
Coca-Cola operates in many cultural contexts where consumer tastes and preferences are quite different. Localizing marketing strategies and product offerings to fit local cultural norms and preferences is both an opportunity and a challenge for the company.
Legal Factors
Coca-Cola has to deal with a complicated regulatory environment pertaining to food safety, labeling requirements, advertising standards, and environmental regulations in different countries. Failure to comply with these regulations may lead to fines, legal issues, and harm to the company’s brand image.
Coca-Cola is also confronted with legal issues pertaining to product liability, intellectual property rights, antitrust laws, and labor laws. Expensive litigation and bad publicity resulted from legal battles can affect the company’s financial performance and brand image.
Major Challenges Affecting Competitive Position
Health Concerns and Changing Consumer Preferences
Coca-Cola is being challenged by health issues and evolving consumer preferences towards healthful drinks. The company is faced with a strategic dilemma of balancing the demand for traditional soft drinks with the rising popularity of healthier alternatives.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Risks
Coca-Cola faces a number of challenges due to compliance with multiple and ever-changing regulatory requirements, as well as legal risks connected with litigation and regulatory scrutiny. Compliance with food safety requirements, environmental laws, and labor legislation in the face of legal intricacies demands systematic control and adequate resources.
Technological Disruption and Digital Transformation
Coca-Cola has opportunities and challenges because of the fast pace of technological innovation and digital transformation. The adoption of digital technologies for customer interaction, process optimization, and innovation is critical in the changing beverage industry environment.
Environmental Sustainability and Water Management
Environmental sustainability issues, including water usage, packaging waste, and climate change mitigation, are a major challenge for Coca-Cola. The long-term viability and corporate responsibility calls for the implementation of sustainable practices and environmental impact minimization throughout its operations and supply chain.
CSR practices
Coca-Cola is dedicated to CSR practices and it is focused on aligning its programs with the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (UN SDGs) to generate significant social and environmental impact. Here’s how the company adheres to CSR practices and contributes to the 17 UN SDGs:
Water Stewardship (SDG 6 – Clean Water and Sanitation)
Coca-Cola has introduced wide-ranging water stewardship initiatives that are focused on recharging water sources and promoting water saving in the communities where it operates. The company has outlined ambitious targets to restore 100% of the water used in its final beverages and give it back to nature by 2030. Coca-Cola also invests in water infrastructure projects, watershed protection initiatives, and community water-based access programs to promote SDG.
Environmental Sustainability (SDGs 7, 12, 13, 14, 15 – Affordable and Clean Energy, Responsible Consumption and Production, Climate Action, Life Below Water, Life on Land)
Coca-Cola addresses its environmental footprint by advocating for energy efficiency, sustainable sourcing of raw materials, waste reduction, and recycling programs. The company targets to have all of its packaging recyclable by 2025 and has pledged to reduce its carbon emissions in its value chain. Furthermore, Coca-Cola provides funding for biodiversity conservation programs and sustainable agriculture practices aimed at reducing the impacts of climate change and conservation of ecosystems.
Community Empowerment
Coca-Cola supports community development programs that target poverty reduction, food security, healthcare access, education, and women’s empowerment. The company, through programs such as the Coca-Cola Foundation, offers grants and support to NGOs and community organizations that are working on social problems and inclusive growth.
Ethical Sourcing and Labor Practices (SDG 8 – Decent Work and Economic Growth)
Coca-Cola practices ethical sourcing and gives a high priority to labor rights and workplace safety throughout its global supply chain. The company is dedicated to fair labor standards, human rights protections, and diversity and inclusion initiatives to provide a safe and respectful work environment for employees and partners.
Youth Empowerment and Economic Development
Coca-Cola sponsors youth empowerment programs, entrepreneurship projects, and skills development opportunities that create economic growth and innovation in communities around the world. The company seeks to provide the young people with the skills and resources that they need to thrive in the twenty-first century economy through partnerships with educational institutions, government agencies, and youth organizations.
Recommendations
Recommendations for Coca-Cola should focus on leveraging its competitive advantages, refining its internationalization strategy, and enhancing leadership and management practices to effectively implement CSR and SDGs within the context of country culture:
Coca-Cola should leverage its strong brand equity and innovation capabilities to create and market healthier beverage choices which are in line with current consumer trends and global sustainability objectives.
Adapting marketing strategies, product offering, and CSR initiatives to represent the distinctive cultural norms and preferences of each country will make Coca-Cola more relevant and competitive in various markets.
Local leadership development investment and nurturing of relevant partnerships with community stakeholders will ensure that CSR programs and SDGs are implemented effectively, thus aligning them with local needs and priorities.
Accountability in reporting of the progress towards CSR and SDG targets and leadership responsibility for sustainability commitment will make Coca-Cola more trusted. Coca-Cola can leverage these recommendations by incorporating them into its business strategy, to improve its competitive advantage, promote sustainable growth, and create positive social and environmental impact at the global level.