Global Strategy and Implementation of Apple Inc.
Apple Inc. is a popular brand with a wide portfolio of products in the consumer electronics and software industry. Apple’s 2023 turnover is estimated to be almost $383 billion. An international corporation, it has more than 100 countries of operation and serves hundreds of millions of customers all over the globe.
Apple, having a workforce of almost 161,000 employees, is one of the reasons behind achieving more innovations and sustained market leadership. In this analysis, we will go into a strategic discussion, trying to develop further opportunities for Apple to expand and develop its business in compliance with its corporate goals.
Read more: Business Project of Apple Inc.
Porter’s Five Forces Model
Analyzing Apple‘s competitive structure in one of its key markets, such as the smartphone industry, using Porter’s Five Forces model:
Bargaining Power of Buyers
Extensive Consumer Choices
There is a plethora of options throughout the smartphone market which is broad and stretches from limited features for a minimal cost, to top-end phones with multiple features. This variety restaurant allows the consumers to choose those smartphones, which are in line with their particular convenience and finances.
Abundance of options tends to intimidate the consumers to fulfill their detailed comparison of specifications, designs, and prices, which in turn oblige the smartphone manufacturers to continuously develop and deliver exceptional features to satisfy and possibly sustain their customers.
Price Sensitivity and Competitive Pricing
A particularly important feature that manufacturers must consider is their price sensitivity; this is caused by a wide array of substitutes – like tablets, new smartphone models, and strong competitive pricing strategies. These aspects might drive the movement of shoppers toward finding better prices to use their money more productively by changing brands to cheaper products.
This context demands eliciting a thoughtful equilibrium of pricing strategies which are contingent upon the product speculations and features which bring about the separation of the brands without hurting profitability.
Demand for Innovation and Customization
With the changing consumer inclinations, there is a notable rise in the trend of asking for revolutionary creations like multiple cameras, performance terminal and 5G data plans, in addition to the user imposed choices of color variation and memory choices.
As smartphone market is shifting, this is an opportunity to reinvent new designs and technology that make these phones not only meeting with the current demand but also anticipating the future needs of the consumers. Today providing up-to-the-minute technology and individualized experiences is imperative when it comes to meeting customers,’ interest and setting products apart from the competitors’ in a highly crowded market.
Empowered Consumers through Online Resources
The tremendous transition from brick and mortar shops to online stores has caused the emerging of ecommerce websites which have made consumers to have the major bargaining power. Through this access to the riches of knowledge, probable purchasers conduct a comprehensive inquiry and uncover all these parameters.
This therefore demands of phone makers to maintain high standards of quality and reliability and still offer competitive pricing to attract customers and have their prevailing products positively compare with those of other companies.
Influence of Telecom Carrier Agreements
Mobile phones of consumers are often purchased via a contract with telecom carriers that typically include different discounts, ranging from subsidized devices to bundled services. Through these agreements, power providers set the rules of the game and shape consumer decisions with preference towards a few specific brands or models being favored by the mass market.
Mobile phone producers have to deal with it effectively as it is crucial to choose the best route distribution, but contracts must be supported by the produced brands. However, such contacts not only affect the consumer’s own choice but also their loyalty to one brand or another and retention as the customer may prefer to stay within the terms of the contracts rather than looking for opportunities elsewhere.
Threat of Substitutes
Competition from Multifunctional Devices
The advent of portables to laptops, and tablets and Wearables that allow their users to move to browsing and multimedia consumption introduces as an important factor the challenge to the smartphone business.
These products because of their diverse features like the larger screens on tablets and the higher computing power in laptops motivate smart phone companies to generate and innovate new products always different to one other in a market which is becoming crowded.
Technological Advancements in Consumer Electronics
Other innovations in the consumer electronics segment in the form of smart watches and smart home appliances comes in so fast that consumers not only modify their choice set but also raises their expectations of any competitor in the industry.
These restless rivalries source phone makers to keep on a continuous flow of research and development in order to create visually distinct products that can compete with even these changes being made to the technology.
Convergence of Technology Leading to Hybrid Devices
The increasing integration of technologies among different sectors, opening up vast connectivity possibilities through the advent of devices that perform both smartphone and other electronic function simultaneously, have resulted in products like foldable devices and AR-enabled technologies.
The situation increases the puzzle of manufacturers who are forced to look into alternative forms and features that are relevant to the tastes and preferences of the changing consumer landscape.
Emergence of Voice Assistants and Smart Speakers
Voice technology with assistants such as Alexa and Siri is decreasing our dependence on smartphones by giving us the ability to communicate with devices via voice for the darks shipped on the terminals. This change is resulting in phone manufacturers vying for a stake now that it looks like the future may be void of interactions directly with devices.
Improving Price-Performance Ratios of Substitutes
As new inventions involves materials or processing techniques in manufacturing, substitutes like tablets and Wearables are becoming less costly and offer higher performance. These developments, which provide smartphone users alternative products that are equal or better in value, oblige smartphone producers to rethink their product strategies by making products that are not only functional but have also better value propositions.
Analysis
The international strategy of Apple may be examined using Porter’s Diamond and Bartlett & Ghoshal’s framework. Such examination takes into account factors such as factor conditions, demand conditions, related industries, firm strategy, structure and rivalry, along with the integration-responsiveness framework. Let’s break down the analysis:
Porter’s Diamond Model
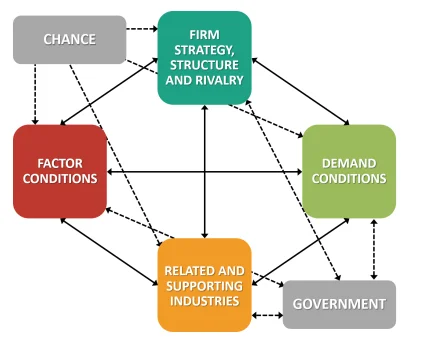
Factor Conditions:
Apple conquers the US market due to the Soviet-level infrastructure and the highest class research institutions like Stanford and MIT. Silicon Valley creates an environment of innovation and gathers the best minds both on the local and global levels. However, Apple’s success also resides in the global approach, which they use to be closer to different types of workers, for example, the research and development, manufacturing, and marketing.
Group work with designers from different cultures must be considered since it brings universal product appeal. The other thing which is worth consideration is that global supplier’s open doors to the supply chain which then allows for the acquisition of specialized skills which are crucial for the supply chain.
Demand Conditions:
Apple’s major operations face a very dynamic situation. The demand is highly diverse both within and outside the company. It offers products that are diverse enough so that they may be the proper fit for consumers with not only high spending capacity but also those with more limited budgets like the iPhone SE. The worldwide Apple products demand is determined by the financial status of consumers as well as technological developments and cultural norms.
For example, in the case of the emerging markets like China and India, where the smartphone penetration increases, Apple is shifting and revising its marketing and product strategies to meet local preferences and to retain the brand image of innovation and quality.
The company makes use of market research and consumer insights to uncover the changing customer needs and choices so as to come up with products that respond to the targets accurately. What is more, Apple’s pricing strategy is the indication of the aiming at the affluent customer segments as well as seeking to include financing for widening the circle of consumers.
Related and Supporting Industries:
Apple’s achievement is transferred into the network of industrial cooperation. In order to establish certainty in its supply chain, the company has built strategic partnerships with important vendors like Foxconn and TSMC, thus securing supply of critical parts such as semiconductors and displays. Through these strategic formulations, Apple can achieve the required levels of product quality and satisfy customers in a timely and efficient manner.
Moreover, developers of software, designers of apps and content producers make up the ecosystem of the Apple, which constitutes the whole value proposition of its products. The App Store serves to be a stage where developers can design a variety of apps that can boost the user experience and have customers come back for more. In addition to that, Apple stores are used to connect with the customers to offer them personalized services, technical support to increase the brand loyalty as well as to improve the customer satisfaction.
Firm Strategy, Structure, and Rivalry:
Apple’s differentiation strategy is implemented by basing its products on innovation, design, and customer experience, which gives its products a unique selling point that distinguishes them from the competitors. The organization’s structure is purposely developed for innovation, teamwork, and agility, ensuring the company remains competitive and ahead in a dynamic environment.
While Apple cherishes its culture of secrecy and insists on the high level of product development, it remains a leader in the industry and gets a competitive edge. Differentiated by such fierce rivalry, Apple enjoys a secure position in the smartphone market due to its robust brand image, loyal customers, and Apple’s own ecosystem of services (iCloud, Apple Music and Apple Pay). Furthermore, the firm keeps on the path of research and development to churn out product innovation and keep its spot as the leading market in the area of technology.
Through the utilization of the identified factors, Apple has become a global industry leader in innovation, design, and the consumer experience, what has been the driving power of the company’s longevity in the ultra-competitive smartphone market and beyond.
Chance in the Mobile Industry
One distinct element in mobile industry that will consistently provide worries and take advantage of them is the factor of chance that brings on both unanticipated challenges and opportunities. One way such companies can gain advantage is via new technological breakthroughs like 5G, AI, and foldable screens which helps them lead in innovation and offers consumers with the opportunity to buy cutting edge device.
Yet the fundamental source of major disturbance, which cannot be predicted, is supply chain disruption from severe weather, pandemics or unrest, that directly impact trading policies. They may result in curtailing in production, compromising production level, and unbalancing market functions.
To be competitive, the mobile companies should be fast, on the lookout all around the globe for events and trends, and they should be able to change anything in their strategies or operations quickly in order to avoid risks and take advantage on any new opportunities.
Government Influence in the Mobile Industry
The Regulations, Policies and Governments have the primary role in molding the operational environment of the mobile industry. Regulations containing aspects related to telecommunications, data privacy, consumer safety, and environment’s effect directly affirms that makers should design, produce, and advertise their product based on the regulations.
Additionally, government gives a contribution in the industry development by initiating programs that encourage the development of technologies and physical structures, thereby enhancing the capacity of companies to develop new innovations and compete internationally. There are challenges, such as political problems or international trade troubles that can generate un-predictability that is very difficult to include in business planning and running the business.
Strict protection of the rights of data subjects, the establishment of rules on their deployment and the protection of privacy, are key issues of data processing regulations, which make an effective operation in this area difficult. We can see now the necessity of mobile companies to work in close cooperation with policymakers and to keep themselves updated to make sure that all legal requirements and local and international laws are met, casing their own business development.
Bartlett & Ghoshal Framework
International Strategy in the Mobile Industry
Based on the design, development and manufacturing core competencies, mobile companies quickly adjust to become market players in foreign countries. At first, they replicate their original products and strategies promoting uniformity throughout world regions as a way of achieving economies of scale and enhancing a single global brand name.
It is a subject of standardization that simplifies the penetration of the market outside the country, using the already established repute of the company and their areas of expertise. Nevertheless, it is the very same companies that in light of the development of the markets frequently use localization strategies in order to adapt their products and services to their consumers’ individual preferences in different regions. Localizing the assortments and engagement strategies by connecting with local cultures, languages, and behaviors of the consumers, brings trueness and triumph of your brand in different markets.
Global Strategy in the Mobile Industry
Global strategy of mobile companies ensures a centralized control by companies over the product development and the branding while including minor local customization, which is meant to meet demands and regulation of particular area. By using this method, a control over the image of global brand and quality of product is achieved.
For instance, online assistants that offer multi-lingual support and content that is territory-specific satisfy local demands whilst remain worldwide liked. While emphasizing global consistency that is, the achievement of economies of scale, the company should however not ignore the local responsiveness taking into account efficiency, market share, and customer experience, worldwide.
Transactional Strategy in the Mobile Industry
Adopting a transnational strategy, mobile companies have the opportunity to create a flexible global network which works as brand’s subsidiaries, research centers, and manufacturing facilities based in, for example, various countries.
This approach allows for redistributing the resources, abilities, and innovations among the regions, each of which still develops its own specific features due to the active work of the cross-culturally spawned teams. By using this approach partnering and shared effort the business is able to customize the plan to local markets and client’s demands. That way they are able to avoid the delays from the supply chain and manage to have a high level of product quality all over the world.
Multidomestic Strategy in the Mobile Industry
The strategy of multidomestic style emphasizes on identifying the customer’s unique needs and corresponding domestic regulations in each market, so that the products can be customized to fit perfectly. Via social media, local prices, new products characteristics, and the message may be modified in accordance with the local nature and target consumers of the company.
This solution is namely increasing customer involvement in product acceptance as well as resolving local complexity for example regions with distinct regulations and consumer tastes. Through a process of bringing the local perspective together with the global overview and supervision, market players can achieve their ultimate goal of being the industry leaders and notching up the most profits, while at the same time ensuring a coherent corporate image to their clients.
External Environment and Challenges
The external environment can be evaluated and the key challenges, which are hindering Apple’s competitive position, can be identified by using the PESL framework, including Political, Economic, Social, Technological, Legal, and Environmental factors. Let’s examine the implications of each of these factors on Apple:
Political Factors
- Trade Policies and Tariffs: Apple is subject to the variation of trade rules and tariffs by being dependent on global supply chains and factory organizing. Take the case of a conflict scenario between the US and China: it can either push Apple’s supply chain costs to the higher side or introduce a delay in production.
- Regulatory Environment: Scrutiny by government authorities, especially regarding data privacy and antitrust issues, can evoke some operational changes and strategic decisions by Apple. Conforming with the specific regulatory requirements in different countries may take effort and resources, which may limit Apple’s creativity or expansion into new markets.
Economic Factors
- Global Economic Uncertainty: An economic slowdown or a decreasing in the consumer spending can lead to the reduction in Apple’s sales, especially for the high-end products. A volatile economic environment in many of Apple’s main markets may cut down the number of buyers and decrease demand for the company’s products and services.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Apple’s business activities worldwide are exposed to currency exchange rate risks, which affect the company’s income and its profitability in international markets. Moving around the exchange rates may freeze the pricing strategies and affect profit margins, and planning becomes a challenging thing.
Social Factors
- Changing Consumer Preferences: Social trends are becoming more and more inclined towards sustainability and ethical consumption, and, consequently, the consumer preferences are being reshaped. Apple needs to consider changing the product portfolio and strategies of marketing, to provide the right means of communication with the consumers and remain their choice.
- Digital Divide: The gap in technology and digital infrastructure availability between countries and developing areas is something that scares Apple in terms of its market reach. Via projects such as inexpensive goods or educational programs, the digital divide can be bridged by Apple and, in consequence, its clientele expanded.
Technological Factors
- Rapid Technological Advancements: The Apple Company has to keep abreast of the speedy technology development, hence it should remain at the cutting edge of AI, AR, and 5G technologies. Not to innovate may means that you will be losing to your competitors in the market share.
- Cybersecurity Threats: Cyber-attacks are the increasing threats in Apple’s networks, these include data breaches, privacy violations and so on. Security remains a paramount factor by ensuring that reliable security measures are in place and the software is continuously being updated to address any vulnerabilities, which can help in preserving the trust of the customers.
Legal Factors
- Intellectual Property Protection: For the Cupertino-based company, intellectual property rights are the very foundation for keeping a competitive position and ensuring that similar devices do not flood the market. The legal battles surrounding patents, copyrights, or trademarks may lead to a loss of money or a brand equity destruction at Apple.
- Antitrust Regulations: The probing of Apple’s dominant market position, especially in the app store sector, can result in lawsuits and regulatory measures. In view of the fact that antitrust regulations are subject to frequent interpretations, Apple has to adjust its business conduct and procedures.
CSR Practices
Environmental Sustainability:
Apple is committed to meeting its carbon neutrality goal by 2030 not only for all its operations but also for the whole supply chain as well. This involves using renewable energy for the company operations and reducing emissions from manufacturing processes. The company makes use of recycled materials in its devices and designs the products while keeping recyclability in mind, such as aluminum and rare earth elements.
Labor Practices and Supply Chain Responsibility:
Apple is very attentive to the well-being of workers who are involved in the production process. The company will provide a safe and fair labor environment. The business in question performs periodic inspections and ensures its partners comply with labor rules.
Diversity and Inclusion
Apple makes sure that the company is an equal-opportunity employer and diverse in its workforce and business culture. The enterprise has launched programs to boost the presence of minority groups, women and people with special needs in the staff.
Community Engagement and Philanthropy
The Apple Giveback and the Apple Community Education Initiatives are some of the programs through which Apple contributes to improving the educational system, protecting the environment, and developing communities.
Supporting UN SDGs
Apple is making its corporate social responsibility (CSR) mission to tackle the world’s problems aligned with the UN’s Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) which include climate change, poverty, and inequality.
Recommendations
In recommending strategies for Apple to enhance its competitive advantage and effectively manage internationalization, leadership, and CSR practices within the context of country cultures and the implementation of CSR and SDGs, several key considerations should be addressed:
Tailored Market Strategies:
That mean Apple should have a localization strategy which should take into account the specific cultural, economic and regulatory features which are represented in each country Apple operates in. This involves tailoring product features, price, and marketing campaigns to suit local consumer demand and the cultural norms of the communities.
Leadership needs to emphasize cross-cultural competence and awareness of the country’s peculiarities so that a communication and a cooperation between local teams and stakeholders is achieved. This comprises funding cultural programs for staff members and creating a conducive workplace atmosphere which appreciates diversity.
Integration of CSR and SDGs into Business Strategy:
Apple must endow CSR and SDGs with the company’s core business strategy, setting corporate goals in line with sustainable development goals and societal needs. This is in the form of considering sustainability in all the design, purchase, and operations of your business.
Leadership should promote and lead by example a corporate citizenship and social responsibility culture, which stresses the significance of integrity in business, environmentally-friendly practices and social engagement. Such targets and performance indicators must be enacted, and reporting on progress towards CSR and SDG targets has to be implemented regularly.
Innovation and Technology Leadership:
Apple should go on increasing its R&D in developing sustainable technologies and adopt tech leadership which should be meant to promote environmentally friendly practices and to contribute to a better society. Embracing the latest technologies to battle global challenges such as climate change, poverty, and inequality is the aim of this process.
The leadership should be supportive of a culture that encourages innovation and risk-taking, expecting employees to continuously come up with new ideas and approaches to tackle complex social and environmental problems. Apart from this, it will also be important to promote innovation via recognition, financing R&D projects, and having the necessary resources in place to enhance these initiatives





